Sickle cell disease (Sickle-cell) is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder. This is due to the fact that a person with this condition has only one copy of a chromosome. As a result, if a person inherits one copy of S.C.D., the disease will occur in that person's body. However, if one inherits two copies of S.C.D., they may pass on one of their chromosomes to an offspring without developing the disease. This means that two individuals are free from having S.C.D..
Sickle cells occur in the bone marrow and blood plasma. If one of these blood vessels becomes infected, the red cells will then be deposited in that area. Sickle cells are an inherited trait that can be passed down from the mother. If a person inherits two copies of S.C.D., they may pass the trait to another family member.
Sickle cells are typically found in adults. Although some people do experience a case of S.C.D., it is not common. In adults, this disease develops in two places in the body – in the bones and in the blood. The symptoms of S.C.D. vary in each person.
In children, sickle cells are more commonly found in the bone marrow. It is usually triggered by infections in this area. When one enters adulthood, sickle cells become apparent in the bone marrow. In children, the symptoms include fatigue, pale skin, weakness and lack of energy. In adults, the symptoms may include weakness, frequent urination and low blood count. In severe cases, these symptoms may cause severe weakness and even paralysis.
Another symptom of S.C.D. is hemolysis. This is the destruction of red cells due to too much iron. Children may develop this symptom as an effect of a sickle cell infection. This is why a child may develop diarrhea or have anemia, when he or she is infected with sickle cells.
Because of its hereditary nature, sickle cells is passed down from one generation to the next. It may be caused by exposure to chemicals such as penicillin. or radiation.
People who suffer from AIDS or cancer may also suffer from this condition, as well as individuals suffering from leukemia or lymphoma
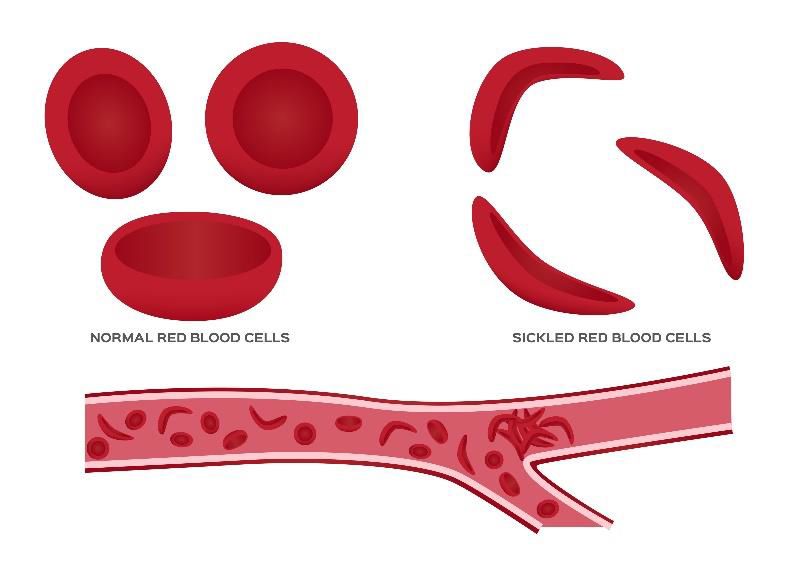
Some symptoms of sickle cells are often confused with some of the other inherited conditions, such as arthritis. However, sickle cells are not curable. People with sickle cells, cannot be treated. The disease does not respond to any type of medication.
For individuals who do not have sickle cells, it is important to know about the different forms of treatments available for the disease. While there is no cure, there are some medications that can control it. The treatment option that a patient should use depends on the individual's condition.
There are certain drugs that can help control the symptoms of the disease and lessen the chance of complications. Medications for S.C.D. may include anti-tuberculosis drugs. Anti-biotics are also effective for controlling and killing the bacteria that causes S.C.D. In addition to antibiotics, there are immunosuppressive drugs such as cyclophosphamide and corticosteroids that can minimize swelling and inflammation.
Surgery may also be used in order to remove the tumor in the blood vessels. or to stop bleeding and to prevent heart attacks. In certain cases, surgery may also be used in order to improve the quality of life of the person with sickle cell disease.
There are also some medications that may help to improve the health of the bones. or muscle tissues. This type of medicine may also help reduce pain and swelling.
Some physicians suggest limiting or avoiding some foods that contain iron, so that people who are taking certain medications, such as antibiotics, do not eat allot of these foods. These foods should not be consumed in any case. Also, people who are pregnant or lactating may not eat these foods.
