Astrocytomas are a subtype of non-small cell lung cancer that can have the appearance of tumors on the skin and other soft tissues. They are caused by tumors of astrocytes (a type of white blood cell) that invade the blood stream through a break in the walls of blood vessels. They are classified into two major groups: primary, and secondary astrocytomas. Primary astrocytomas may have several precursors in the bone marrow before forming an invasive tumor.
Many different types of tumors develop in the body, many of which are asymptomatic. Most tumors go away on their own. Some tumors are malignant and cancerous, and some are benign. Some tumors, such as cysts or abscesses, need to be surgically removed. The most common tumors in the body are malignant.
There are four different types of astrocytic tumors. They are: diffuse, bone marrow and focal. Diffuse astrocytomas are most common, usually affecting one part of the body, such as the chest. Tumors often grow quickly or do not grow at all for months or years. In some cases, treatment is possible in some cases (for example, with diffuse neurofibroma), while in other cases, treatment has no effect.
Medullary tumors can affect different parts of the body. Most often, they affect the bladder, esophagus, stomach and pancreas. Some of them can spread to other organs and cause serious complications, such as pancreatic cancer.
Focal astrocytomas are the most serious type of astrocytoma. They are the most aggressive of the three types and also some of the most difficult to treat. Because these tumors do not spread, they are not easy to find. However, they are more likely to cause significant damage to the body.
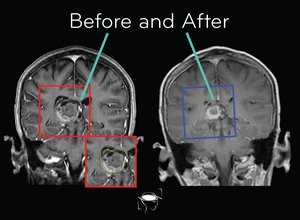
Focal astrocytomas are very dangerous because they grow in the central nervous system of the body. They invade nerve tissue and cause pain, seizures, and even brain damage. They are very difficult to remove and sometimes require surgery. Focal tumors can grow in areas of the brain where there is no growth in other parts of the body.
Primary astrocytomas are less likely to spread and have a slower rate of growth than other types. They do not involve the nervous tissue and therefore do not need surgery. The symptoms of these cancers often disappear on their own within a few months. However, these tumors can become malignant if they are left undiagnosed or untreated. This is why they are very dangerous and should be removed immediately if detected.
If your doctor suspects that you may have an astrocytoma, he or she may refer you to a specialist who will test your blood for cancer cells, to see if they are non-cancerous tumors. Non-cancerous tumors are always tested before treating them. If the tests come back positive, you may be referred to a treatment center for more extensive treatment. Depending on the case, you may need surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of the two. You will need a hospital stay, but the treatment will depend on the type of tumor and your medical history.
In rare cases, people who have had chemotherapy may have some residual effects that cannot be seen by X-rays. If this happens, the doctors will have to perform more tests. This is why it is always best to consult a doctor before undergoing chemotherapy.
Radiation therapy can either be in the form of a pill, injection, or surgery. It usually takes many weeks to see the benefits of radiation therapy.
Surgery is another form of treatment. There are three types of surgery; laparoscopy, palliative surgery, and endoscopic surgery. Laparoscopic surgery requires the surgeon to make a small incision near the tumor and to place a camera through the hole and watch your tumor.
Endoscopic surgery involves removing the tumor with the use of anoscope. There is still more surgery needed, but it usually makes the cancer go away permanently.
